Development and application of ATP bioluminescence technology
ATP is an abbreviation for the chemical substance adenosine triphosphate, which is present in all organisms (from microorganisms to higher animals). The main role of ATP in the body is to provide energy. Given that ATP is present in all organisms, the detection of ATP using an ATP luminometer can indirectly demonstrate the presence of an organism. With the increasing demand for food hygiene quality in the food industry, and the ATP bioluminescence method is simple, rapid and sensitive in detecting food microorganisms, it has received extensive attention in recent years.
1 Development process of ATP bioluminescence technology
ATP bioluminescence technology was born in the mid-1970s. In 1983, Moyer [1] first proposed that the content of endogenous ATP in cells can reflect the activity of cells and the number of living cells. In the same year, Gronroos [2] also confirmed that this technology is a reliable and sensitive method for determining cell viability. In the 1980s, the British first developed the ATP detector detection system, which was later developed into Europe, the United States, and Japan. Applications range from food processing, supermarkets and the catering industry to microbiological and food residues. In 1998, the Japanese Parliament enacted the Law on the Temporary Measures for the Management of Food Manufacturing Processes, which included the application of the ATP detector detection system. In 1999, Japan also established the ATP Smear Inspection Research Conference, which specializes in the use efficiency and application of this method. One of its contents is to solve the problem of on-site microbial detection in the field of food hygiene monitoring. At the end of the 20th century, some ATP detector detection systems and technologies were introduced to China. So far, apart from the equipment of some provincial health supervision and inspection units, they have mainly been tested and used by some foreign-funded or joint ventures. In 2002, the Ministry of Health of China issued a HACCP implementation guide for food processing enterprises to encourage food processing enterprises to introduce ATP detection systems. In recent years, luciferase has been produced through genetic engineering, and the price has been greatly reduced. With the miniaturization of related instruments, ATP bioluminescence technology will be rapidly popularized in related industries in China [3] .
2 ATP bioluminescence colony count comparison with traditional methods
2.1 ATP bioluminescence colony count
ATP is widely present in a variety of living organisms, and live cells also contain ATP. After the bacteria die, they will be quickly decomposed under the action of intracellular enzymes. ATP bio-fluorescence detection is designed based on the luminescence mechanism of bioluminescent systems. Fireflies have special luminescent substances - luciferin and luciferase. Fluorescein is easily oxidized. It is activated by ATP under luciferase catalysis. In combination with oxygen, the electrons in the fluorescein molecule transition to a high energy level, in an unstable excited state, and when the electron jumps back to a low energy level, it emits a fluorescent photon. The intensity of the light is proportional to the amount of ATP contained in the substance to be detected, and the intensity of the light is measured by a highly sensitive instrument for quantitative analysis. Therefore, by measuring the concentration of ATP in the sample, the number of viable cells can be estimated. The detection steps of the bioluminescence method generally include: cotton swab sampling, sample extraction, addition of fluorescein and luciferase mixture, determination of bioluminescence, standard curve, concentration and viable count. Usually, the surface of the bacteria is surrounded by cell membranes and cell walls, so the sample cannot be measured without treatment. In the measurement, the sample and the microorganism are first mixed with the extraction reagent to open the cell membrane and the cell wall, and the ATP extraction reagent is extracted as a special reagent based on the surfactant. Then, with the fluorescein and luciferase bioluminescent reagent, the amount of bioluminescence reacted with the luminescent reagent is measured by a fluorometer [4] .
This method can be automated, with high sensitivity, and can reach 10-12 mol/L. The detection speed is fast. Compared with the surface dish culture method, it takes only ten minutes to complete a sample test. The detection range is wide. It can detect not only microorganisms, but also the cleanliness of food production equipment, the fermentation activity of yeasts, lactic acid bacteria, and the like. Shenyang Zhongke Yuma Biological Engineering Co., Ltd. introduced the invention patent of “New strain of bactericidal gene-containing strain and luciferase production method†from the Institute of Genetics and Development of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and successfully developed “ATP fluorescence†with independent intellectual property rights in China. The system uses the advanced ATP bioluminescence technology. As long as the relative fluorescence value is measured, according to the standard curve of the relative fluorescence value and the total number of bacteria, the total number of bacteria in the sample can be quickly obtained within a few minutes [ 5] . In 2008, Zhou Aiyu et al. developed a handheld ATP bio-fluorescence detector and achieved good results [6] . The picture below is two different types, the left side is called the handheld ATP illuminometer detector, making the detection more convenient. (pictures are from the internet) 
2.2 Traditional Colony Technology
For the determination of the total number of colonies, generally, the test sample is made into several different 10-fold incremental dilutions, and then 1 mL of each dilution solution is separately taken and placed in a sterilization plate and mixed with the nutrient agar medium at a certain temperature. After a certain period of incubation (usually 48 hours), the number of colonies formed in each dish was recorded, and the total number of bacterial colonies contained per gram (or per ml) of the original sample was calculated based on the dilution factor. (The pictures below are all from the Internet)
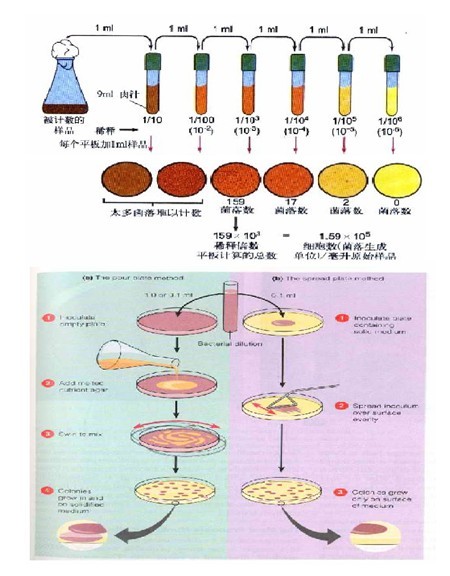
3 Application of ATP bioluminescence technology
ATP bioluminescence has a wide range of applications and is now used in many areas of the food industry. Studies have shown that ATP bioluminescence has a good correlation with the standard bacterial culture colony counting method (r = 0.98) [7] , but how to subdivide the bacterial species is difficult, and a lot of work is needed. . This method can be used to quantify the content of microorganisms in food materials, meat, aquatic products, vegetables, beverages, alcohol, yogurt, and the like. In addition, the ATP bioluminescence method can be used to quickly and easily detect the cleanliness of the food production environment. The detection of the ATP content is represented by a Relative Light Unit (RLU). As the RLU value decreases, the probability of microbial detection also decreases. The experiment proves that if the RLU value is limited to 100-1000, the RLU value is less than 100, the microbial detection probability is 0, and when the RLU value is in the range of 100-1000, the microbial detection probability is 30%, and the RLU value exceeds 1000. The probability of microbial detection was 96%. According to this result, in the daily detection of the cleanliness of the food production equipment or the close contact with the food, the RLU value below 100 can be regarded as safe, and the RLU value is considered to be taken into consideration when it is in the range of 100 to 1000. Note that RLU values ​​above 1000 are considered to be at risk of microbial contamination [8] , so ATP bioluminescence is well suited for cleanliness testing of HACCP systems. In addition, it can also be used to compare the sensitivity of yeasts to toxins [9] . In recent years, ATP bioluminescence technology has been highly praised at home and abroad, and is widely used in the quality inspection and control fields of the food industry in the United States and Japan, effectively promoting food production enterprises to improve production efficiency and economic benefits. With this method, continuous improvement and improvement Bioluminescence method is expected to develop into an ideal microbiological detection method and be widely used to continuously improve product quality and ensure food quality and safety.
references
[1] M JD, J H. Nucleoside triphosphate specificity of fireflyluciferase [J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1983, 131(1): 187-189.
[2] GRONROOS M, MAENPAA J, NIEMINEN AL, et al. Correlation of steroid receptor contents with medroxyprogesterone and tamoxifen effects in endometrial cancer assayed by barin vitro ATP-bioluminescence method [J]. Journal of Steroid Biochemitry, 1983, 19(1 ): 194.
[3] Wu Ji, Wang Yan, Zhang Jianjun. Rapid detection of total number of colonies in beer by ATP bioluminescence method[J]. Henan Science, 2006, 24 (1): 63-65.
[4] Liu Bingzhi, Zhu Wei. Application of ATP Bioluminescence in Microbial Testing[J]. Journal of Preventive Medicine Information, 1999, (15) 1:29-30.
[5] Shi Shuai. ATP Fluorescence Rapid Inspection System for Rapid Detection of Total Bacteria[J]. Food Safety Guide, 2008, 1:51-52.
[6] Zhou Aiyu, Luo Jinping, Yue Weiwei et al. Development of handheld ATP biofluorescence detector [J].2008,214:543-546.
[7] Shu Baihua, Sun Danling, Wang Shengli. Study on Rapid Analysis Technology of Bacterial Contamination of Meat Foods[J].China Public Health,2003,19(4):483-484.
[8] Wang Wei. Application and Prospect of ATP Fluorescent Microbial Detection in the Field of Food Hygiene Monitoring[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 2004, 16(3): 266-267.
[9] SA, ML D, P S. Use of ATP measurements by bioluminescence to quantify yeast's sensitivity against akiller toxin [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2003, 495: 217-224.
Kegel Ball
Spice Novelties Co.,Limited , https://www.wholesale-adult-toys.cn

