Urinary microalbumin: early distress signal of the kidney
The survey shows that the incidence of chronic kidney disease in China has increased year by year, the incidence of chronic kidney disease is 10% to 13%, and there is one case for every 10 people in the city. The early stage of kidney disease is not painful or occult, so it is also called "silent killer". The incidence of early edema and hematuria is less than half. Even if it occurs, it often disappears within a few days or a week, so it is easy to be ignored.
In 1982, Viberti et al found that the total protein in the urine of diabetic patients was in the normal range, and the increase in urinary albumin excretion first proposed the idea of ​​urinary microalbumin, and pointed out that the appearance of this protein is an early sign of nephropathy. The detection of urinary microalbumin in many testing methods and testing items is the most sensitive and reliable indicator for early detection of nephropathy. Through the examination of urinary microalbumin, combined with patient history, morbidity, symptoms, and other laboratory indicators, The cause of microalbuminuria in urine can generally be determined.
First, why check the urine routine, but did not find kidney damage early?
To understand this problem, it is necessary to understand what the protein is routinely tested for urine.
Protein in urine routine refers to total protein in urine .
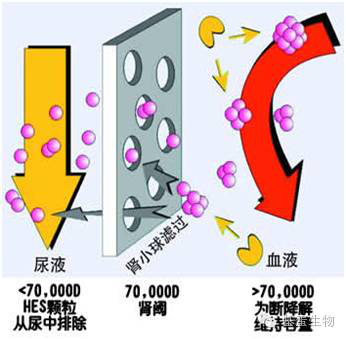
Due to the glomerulus, the pore barrier (normal filtration membrane can pass 70kD molecules) and the charge barrier (with negative charge), under normal circumstances, protein can not be filtered into the original urine through the glomerulus, only a very small number of proteins will enter In the original urine, after reabsorption by the renal tubules, the protein in the urine is minimal. In normal people, the protein in the urine routine should be negative. Due to the methodological limitations of total urine protein determination, the qualitative and quantitative sensitivity of total urine protein are low, so this indicator is mainly used for physical examination. Therefore, when the kidneys are damaged early, the urine contains a trace amount of protein, but it is limited by the limitations of the conventional urine measurement method, and early damage to the kidney cannot be found early, thus missing the early intervention.
Second, microalbumin: small indicators of great significance

Microalbuminuria refers to the appearance of trace albumin in the urine. Albumin is a normal protein in the blood, accounting for about 60% of total plasma protein. Microalbunminuria (mAlb) means that the excretion rate of urinary albumin exceeds the normal range, but is lower than the urine protein level detectable by conventional methods. Its content is 20-200mg / L (random urine), if it can be treated in time, the kidney damage is in a period of reversible.

The content of albumin in the urine of normal people is less than 20mg/L. When the kidneys are damaged early, the content of microalbuminuria in urine is 20-200mg/L. At this time, the kidney damage can be reversed, and the kidney can be completely repaired. Small balls that eliminate proteinuria. At this time, urine monitoring of urine protein often shows negative (-) or (+-), that is, urine is difficult to detect low levels of albumin. When urinary mAlb is greater than 200mg/L, urine routine test urine protein positive (+) ~ (+++), at this time it is proved that the body has a large amount of albumin leakage, the development of kidney disease is only one step away from the irreversible period, if not timely When you are treated, you will enter the uremia period.
Third, the clinical significance of microalbumin
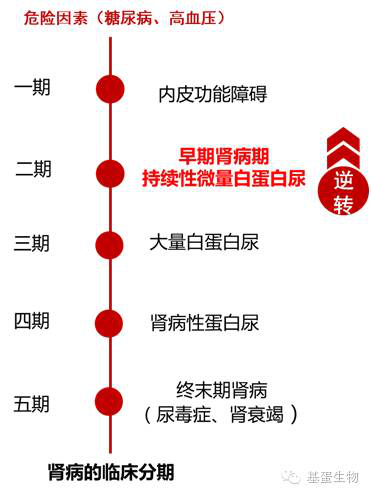
1. mAlb is an early marker of kidney damage
Due to the filtration of the glomerular filtration membrane and the reabsorption of the renal tubules, only a very small amount of albumin is excreted in the urine under physiological conditions. Glomerular capillary endothelial damage can cause albumin to ooze out of the bloodstream into the urethra and into the urine. The appearance of microalbuminuria is one of the indicators for the early diagnosis of kidney disease before the positive expression of urine protein. At this time, the kidney injury is still in a reversible period.
2. Characterization of early kidney damage in diabetic nephropathy and hypertensive nephropathy
Hypertension and diabetes are the main causes of microalbuminuria in urine. In these patients, the detection rate of microalbuminuria is significantly higher than that of the general population. A large number of studies have confirmed that type 2 diabetes is a risk factor for cardiovascular events and death, cerebrovascular events and death, end-stage renal disease and death, and combined with hypertension is more serious. Nearly half of type 2 diabetes has hypertension. In type 2 diabetes, the amount of urinary albumin is a risk factor for death. As the concentration of urinary albumin increases, the survival rate of patients decreases, and microalbuminuria is the earliest clinical evidence of diabetic nephropathy.
3. Independent risk factors for cardiovascular events
Urinary microalbumin is not only an early marker of kidney damage, but also a marker of systemic endothelial cell damage. The presence of microalbuminuria often suggests that the pathophysiological process of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease has been initiated, and the incidence and mortality of cardiovascular disease are associated with increased mAlb. A population survey of 23,964 patients in the United Kingdom showed that microalbumin is an absolute high risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and mAlb and proteinuria are significantly associated with cardiovascular mortality.
4, other
Transplantation of kidney damage caused by various reasons often has changes in micro-urine protein components before significant proteinuria. The recovery of transplanted kidney after renal transplantation also found that creatinine results can not accurately reflect the function of transplanted kidney, and combined detection of urine microprotein It is simple and sensitive, which helps to accurately determine the location and extent of graft injury in the early stage.
Pregnant women with pregnancy-induced hypertension often have no or very few symptoms and signs of kidney damage in the early stage. The sensitivity of urine protein and serum creatinine and urine function tests are low, and no abnormalities are found. Detection of urinary mAlb helps to monitor the degree of renal damage in pregnant women with pregnancy-induced hypertension and the diagnostic grading of pregnancy-induced hypertension.
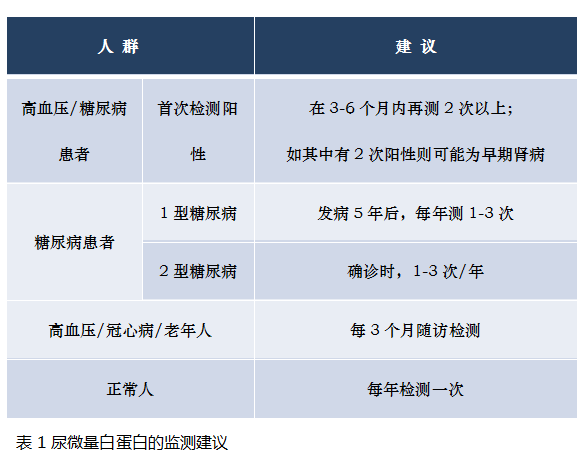
Fourth, monitoring of urine microalbumin
Increased urinary microalbumin content is common in primary nephropathy (such as glomerulonephritis), diabetic nephropathy, hypertensive nephropathy, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis nephritis, etc. The increase in nephritis is particularly significant, and the degree of elevation is related to the degree of glomerular damage. In addition, elevated urinary albumin is also closely related to the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and the occurrence of metabolic syndrome. For tubular damage, urinary microalbumin is generally normal or slightly elevated. International cardiovascular physicians routinely evaluated microalbuminuria in hypertensive patients and found that this value may be higher, up to 58.4%. The study included 2473 Chinese patients, and the urine microalbumin detection rate was 42.9%. The above studies have shown that the detection rate of microalbumin is high in patients with hypertension and/or diabetes, and the trend may be more serious in Chinese patients.
references
SUN Ning-ling, GUO Xiao-wei, LIN Shan-xi, et al. Screening intervention of microalbuminuria in patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus Chinese expert consensus[J]. Chinese Journal of Hypertension, 2012(5).
Böhm M, Thoenes M, Danchin N, et al. Association of cardiovascular risk factors with microalbuminuria in hypertensive individuals: the i-SEARCH global study. [J]. Journal of Hypertension, 2007, 25(11): 2317-24.
Chinese Medical Association Diabetes Branch. Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in China (2013 Edition) [J]. Chinese Journal of Diabetes, 2014, 30(8): 26-89.
Zhan Hong. Clinical significance and diagnostic value of urinary microalbumin [C]// Clinical Psychosomatic Diseases 2015 Seminar Comprehensive Journal. 2015.
FAN Shizhen, CHEN Anbin, LIN Songqing. Significance of Urinary Microalbumin in Early Diagnosis of Hypertension and Diabetic Nephropathy[J]. Chinese Journal of Laboratory Diagnosis, 2013, 17(2): 304-306.
YT-T15
YT-T15
Shenzhen Sunshine Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.shenzhenyatwin.com