Normally cultured cells have low autophagy activity and are not suitable for observation. Therefore, artificial intervention and regulation of autophagy must be performed. The reported drug drugs are:
I. Autophagy inducer
(1) Bredeldin A / Thapsigargin / Tunicamycin : Simulating endoplasmic reticulum stress
(2) Carbamazepine/ L-690,330/ Lithium Chloride (lithium chloride): IMPase inhibitor (ie Inositol monophosphatase, inositol monophosphatase)
(3) Earle's Balanced Salt Solution: Making Hunger
(4) N-Acetyl-D-sphingosine (C2-ceramide): Class I PI3K Pathway inhibitor
(5) Rapamycin: mTOR inhibitor
(6) Xestospongin B/C: IP3R blocker
Second, autophagy inhibitors
(1) 3-Methyladenine (3-MA): (Class III PI3K) hVps34 inhibitor
(2) Bafilomycin A1: Proton pump inhibitor
(3) Hydroxychloroquine: Lysosomal alkalizer (lysosomal lumen alkalizer)
In addition to the selection of the above-mentioned tools, it is generally necessary to intervene in autophagy-related genes in combination with genetic techniques: including antisense RNA interference technology (Knockdown), screening of mutant strains, and introduction of foreign genes.
Third, the autophagy process for observation and detection
After the cells are induced or inhibited, the autophagy process needs to be observed and detected. Common strategies and techniques are:
1. Observe the formation of autophagosomes
Since autophagosomes belong to the subcellular structure, they are not visible under ordinary light microscope. Therefore, direct observation of autophagosomes should be performed under transmission electron microscopy. Phagophores are characterized by a crescent-shaped or cup-shaped, double-layer or multi-layered membrane that has a tendency to surround the cytosolic composition. Autophagosomes (AV1) are characterized by a vacuole-like structure of a bilayer or multilayer membrane containing cytosolic components such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, and the like. Autophagy lysosomes (AV2) are characterized by a monolayer membrane in which the cytosolic component has been degraded. (autophagic vacuole, AV)
2. Using GFP-LC3 fusion protein to trace autophagy formation under fluorescence microscope
Because the electron microscope takes a long time and is not conducive to the formation of monitoring autophagy, people have developed this technology by using LC3 to aggregate during autophagy formation. When there is no autophagy, the GFP-LC3 fusion protein is dispersed in the cytoplasm; when autophagy is formed, the GFP-LC3 fusion protein is translocated to the autophagosome membrane, and a plurality of bright green fluorescent spots are formed under a fluorescence microscope. In an autophagosome, the level of autophagy activity can be evaluated by counting.
3. Western Blot was used to detect changes in LC3-II/I ratio to evaluate autophagy formation.
When autophagy is formed, cytosolic LC3 (ie LC3-I) will enzymatically cleave a small segment of the polypeptide and transform it into an (autophagosome) membrane type (ie LC3-II). Therefore, the ratio of LC3-II/I ratio can be Estimate the level of autophagy.
(Note: LC3 antibodies have a higher affinity for LC3-II and can cause false positives. Methods 2 and 3 need to be combined, taking into account the effects of lysosomal activity.)
4. Detection of long-lived protein batch degradation: non-specific
5, MDC (Monodansylcadaverine, single dansyl cadaverine) staining: including autophagosomes, all acidic vacuoles are stained, it is non-specific.
6, CellTrackerTM Green staining: mainly used for double staining, but it can stain all vacuoles, so it is also non-specific.
4. Localization of autophagy-related proteins
When studying autophagy-related proteins, they need to be localized. Since autophagosomes are closely related to lysosomes, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi, some tracer proteins are commonly co-localized under fluorescence microscopy for differentiation:
Lamp-2: a lysosomal membrane protein that can be used to monitor the fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes.
LysoTrackerTM Probe: Available in red or blue to display all acidic vacuoles.
pDsRed2-mito: vector, which expresses a fusion protein (red fluorescent protein + mitochondrial matrix localization signal) after transfection and can be used to detect the degree of autophagy of mitochondria (Mitophagy).
MitoTraker probe: specifically displays live mitochondria, and fluorescence remains after fixation.
Hsp60: localizes to the mitochondrial matrix and is not released when cells die.
Calreticulin: the endoplasmic reticulum
(Note: These proteins are cytosolic proteins. Cells that are scrambled or trypsinized must be permeablized before immunofluorescence and can be treated with 0.1% SDS.)
Double Packed Mottled Waxy Corn
Eating more corn can increase the brightness of our eyes. Because corn is rich in substances such as carotenoids and these can be said to be used as ingredients for brightening the eyes, eating a proper amount of corn can help to slow down the loss of our eyesight.
And corn is rich in nutrients, with protein, body fat, tapioca starch, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, vitamin B6, vitamin A, vitamin E, carotene, methyl cellulose and calcium, phosphorus and iron. According to research, fresh corn contains 4-5 times more body fat than rice and flour, and contains unsaturated fat, of which 50% are fatty acids, which inhibit the digestion and absorption of cholesterol. It is an excellent medicine for long-term use to reduce blood cholesterol and soften blood vessels, making it an ideal vegetable oil for patients with hypertension, coronary heart disease, obesity and the elderly.
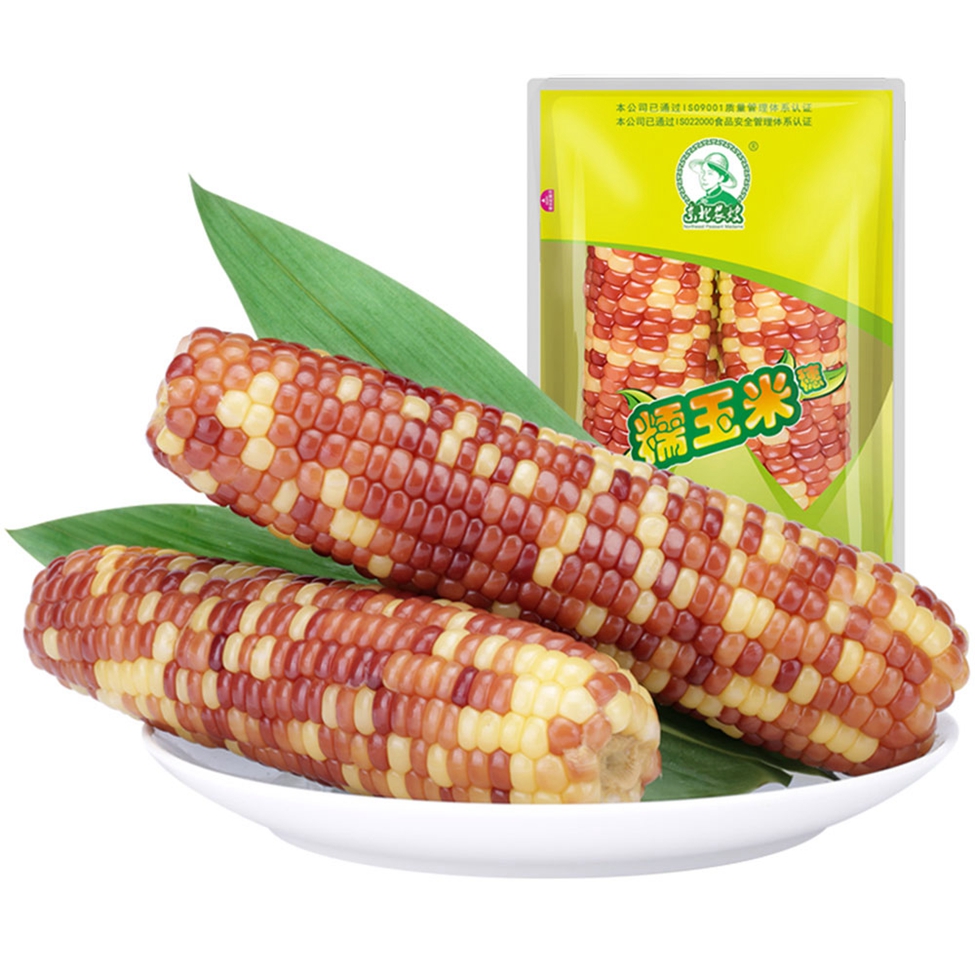

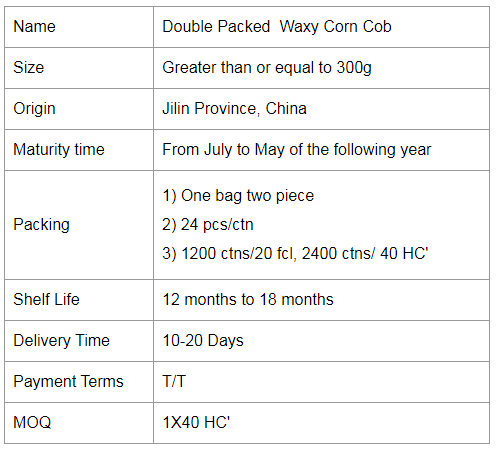
Colorful Gluten Corn,Colorful Gluten Waxy Corn,Colorful Gluten Glutinous Corn,Double Packed Mottled Waxy Corn
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nscorn.com

